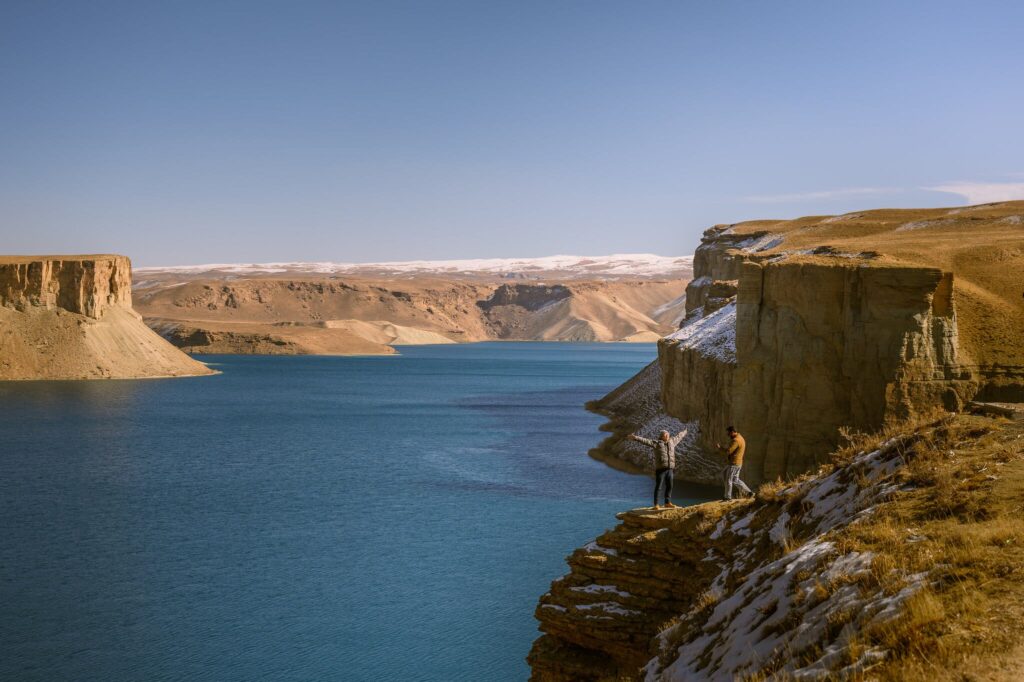
Review of Afghanistan developments
Since the late 20th century, the tourism industry has developed into a significant and expanding phenomenon, experiencing even more rapid growth in the 21st century. Currently, tourism holds a vital position in the economies of numerous nations and, particularly in developing countries, it significantly contributes to the enhancement of economic, social, and cultural frameworks. Nevertheless, if this expansion persists without careful planning and adherence to sustainable practices, it may result in adverse effects on resources, ultimately diminishing the appeal of tourist destinations and causing environmental harm and detrimental impacts on local communities.
Despite Afghanistan’s abundant cultural and natural attractions, as well as its historical heritage, data concerning international tourist arrivals and revenue indicate that the nation has yet to capitalize on this potential. While the influx of foreign tourists to Afghanistan has risen considerably since the Taliban’s return, primarily due to improved security, the country still holds a minimal portion of the tourism sector in comparison to global and regional averages.
Afghanistan, known for its historical significance, vibrant culture, and breathtaking natural scenery, has suffered from years of civil strife, foreign occupation, and instability. However, it possesses all the necessary components to foster a thriving tourism sector. Despite the country’s tumultuous past and the prevailing perceptions surrounding it, expectations for leisure activities in Afghanistan are low; yet, the truth is quite different. Historically, Afghanistan has attracted numerous foreign tourists, with renowned explorers like Marco Polo having traveled through its lands.
Nonetheless, the instability and unique circumstances of recent decades have significantly affected the tourism sector, presenting numerous challenges such as ensuring comprehensive security and social order, efficiently managing natural and historical resources, developing infrastructure, and promoting tourism. These matters must be resolved for Afghanistan to emerge as a favored destination within the tourism industry.
History
The tourism sector in Afghanistan has experienced a fluctuating history. Over the last several decades, the nation has drawn visitors with its diverse cultural, historical, and natural sites. From the 1950s to the 1970s, Afghanistan emerged as a favored location for Western travelers, owing to its comparative political stability and investments in tourism infrastructure. Throughout this era, a multitude of hotels, restaurants, and tour operators emerged in cities like Kabul, Bamyan, and Herat. Archaeological excursions to historical landmarks and, to a lesser degree, skiing in the mountainous regions gained popularity.
Furthermore, Afghanistan was recognized as one of the destinations along the renowned “Hippie Trail.” This pathway originated in Europe, traversed through Iran and Afghanistan, and concluded in India and Thailand. The term “Hippies” referred to a cohort of Western youth characterized by distinct behaviors and ideologies, who journeyed extensively to Afghanistan during the 1960s and 1970s. Nevertheless, this route was halted following the coup in Afghanistan on September 7, 1978.
Afghanistan serves as a prime example of a nation where cities possess significant potential for the expansion and advancement of the tourism sector, featuring both natural attractions and ancient historical sites. Notable cities such as Balkh, Mazar-e-Sharif, Bamyan, Herat, Kabul, and Kandahar are key historical locations that exhibit a considerable range of climatic and geographical diversity: the ruined Buddha statues of Bamyan and the ancient city of Gholgala hold particular cultural and spiritual significance. Herat, renowned for its Grand Mosque, historical minarets, and Goharshad Madrasa, stands as a treasure of Timurid culture and artistry. Balkh, home to the tomb of Khwaja Abu Nasr Parsa and the Zadian minarets, has maintained the essence of its historical legacy, while the Blue Mosque in this province is regarded as one of the most exquisite examples of Islamic architecture in the area. Kabul, featuring the National Museum of Afghanistan, the historical Dar-ul-Aman palace, and the tomb of Timur Shah Durrani, encapsulates a portion of Afghanistan’s political and cultural heritage.

Additional points of interest encompass the Amir Dam located in Bamyan Province, the unspoiled landscapes of Nuristan, and the Panjshir Valley. The city of Ghazni, renowned for its historic minarets, the burial site of Sultan Mahmud of Ghazni, and its medieval Islamic structures, occupies a significant position in the annals of Islamic civilization.
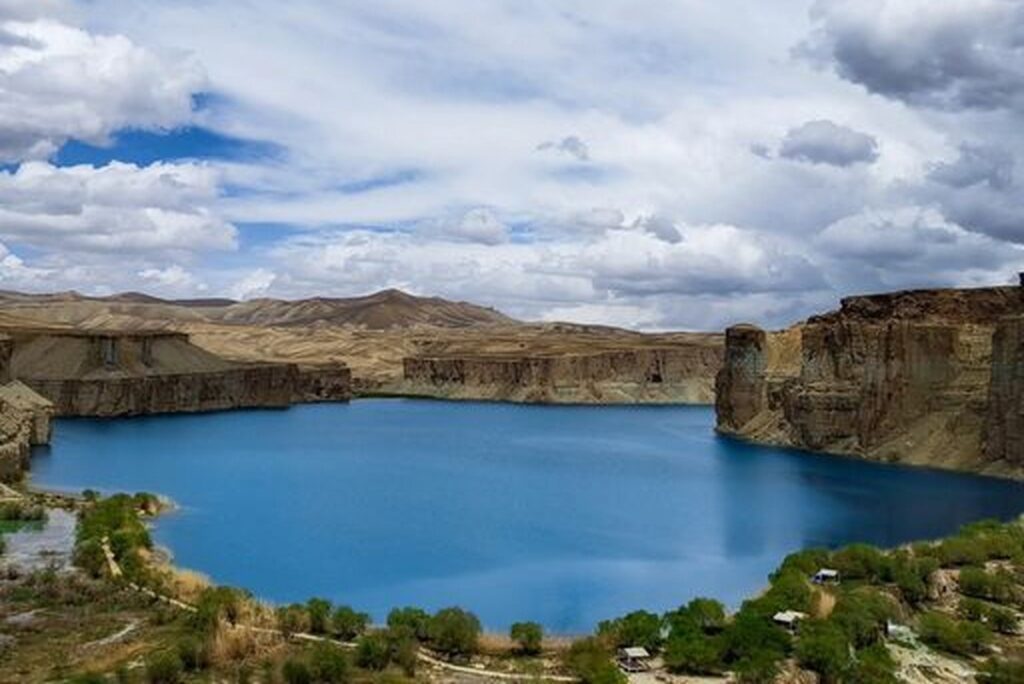

Additionally, local music and handicrafts, including carpet weaving, kilims, and pottery, serve as cultural symbols of the Afghan people. Having a history spanning several thousand years, cities that have served as capitals for powerful governments, along with their esteemed status in science, literature, and art in the East, possess significant potential to turn Afghanistan into a sought-after destination for international tourists.
The role of the tourism industry in the development of Afghanistan
Economic growth
Tourism, recognized as one of the largest industries globally, has the potential to greatly influence Afghanistan’s GDP and enhance government tax revenues. Furthermore, the foreign exchange generated from tourism can be allocated to different sectors, thereby aiding in the country’s continued economic development. This industry is interconnected with numerous economic sectors, including transportation, accommodation, food, energy, culture, arts, and small enterprises, which will foster inclusive economic growth.
Enhancing global commerce and drawing in overseas investment
The connection between the tourism sector and the attraction of foreign investment is a reciprocal and dynamic one, capable of producing substantial economic, social, and cultural effects on a nation. The tourism sector can serve as a catalyst for drawing in foreign investment. As this sector expands, the demand for infrastructure such as hotels, restaurants, and transportation systems increases, providing a compelling incentive for foreign investors to engage in infrastructure projects. Furthermore, if this sector is safeguarded and effectively managed, tourism can project a favorable image of the country globally, which is instrumental in promoting Afghanistan and fostering trust among foreign investors.
Enhancing infrastructure and generating employment
The advancement of tourism can result in enhancements to Afghanistan’s infrastructure, encompassing transportation, lodging and hospitality, public services, administrative and security measures, as well as cultural and recreational facilities, all of which also provide advantages to the local community.
The tourism sector holds the promise of generating millions of significant and impactful employment opportunities in Afghanistan, offering prospects for young people, ethnic minorities, women, and marginalized communities. This job creation can contribute to alleviating poverty and enhancing economic conditions across various regions of the country.
Upgrading urban and rural areas
The tourism sector has the potential to enhance the competitiveness of urban areas and motivate individuals to invest in the growth of cities. Such initiatives can result in better infrastructure and an elevated quality of life for residents. Conversely, the advancement of rural tourism can contribute to economic diversification in villages, generate employment opportunities for various segments of the population, and aid in the preservation of historical sites and cultural heritage in rural regions.
Promoting artisanal crafts
As the tourism industry evolves, artists and artisans have the opportunity to generate income by marketing their products to tourists. In Afghanistan, where individuals face poverty stemming from water scarcity and insufficient modern agricultural practices, this sector presents a valuable chance for local residents to showcase their handicrafts to visitors with minimal training. This industry has the potential to enhance the handicraft sector, promote Afghan culture, and bolster the local economy.
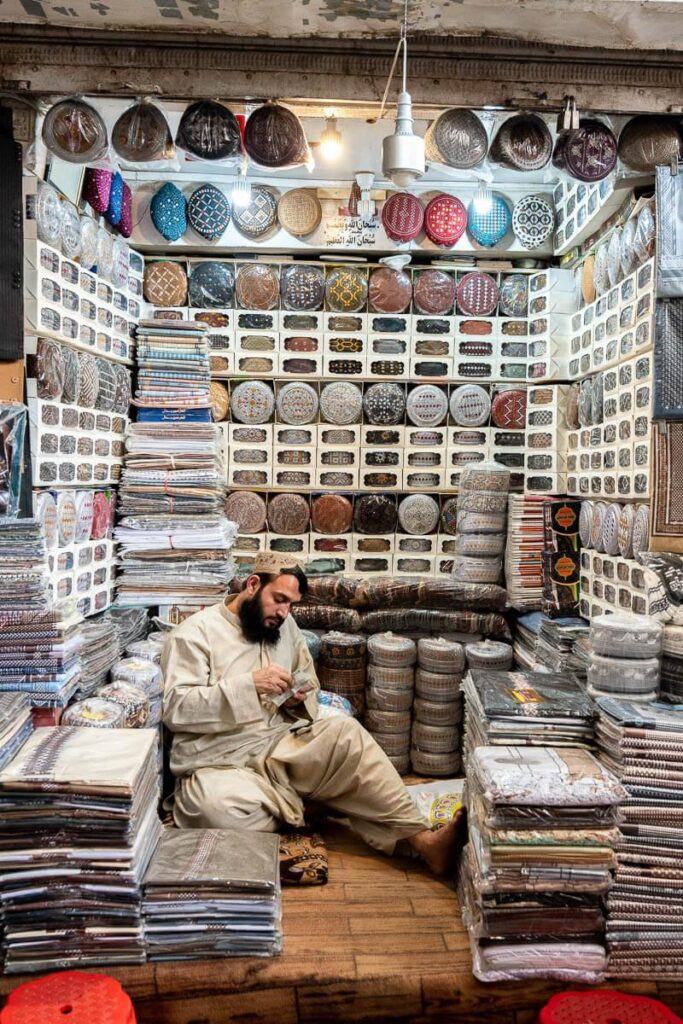

Cultural advancement and interchange
When travelers come to Afghanistan, this reciprocal engagement between cultures promotes mutual comprehension and diminishes cultural biases. These interactions can also result in the establishment of intercultural collaboration and, over time, contribute to the reinforcement of national identity, the preservation and revitalization of cultural heritage, and the enhancement of Afghanistan’s international reputation in the perception of the global community.
Related articles:
The role of education in reducing social harms in Afghanistan
Conclusion
The tourism sector has the potential to significantly contribute to economic growth and social advancement in Afghanistan. The influx of tourists into Afghanistan will enhance industries such as hospitality, transportation, handicrafts, and services, thereby creating more job opportunities and increasing income generation. Ultimately, this development will result in a decrease in poverty levels and an enhancement of living standards for local communities.
Nonetheless, to fully harness this potential, it is essential to make strategic investments in tourism infrastructure, which encompasses roads, airports, lodging, and various amenities, in order to ensure a positive, secure, and appealing experience for both domestic and international travelers.
Alongside physical development, it is crucial to train specialized human resources, enhance service quality, and comply with international standards for the advancement of this industry. In this context, focusing on various forms of tourism, particularly domestic and religious tourism, has the potential to foster economic growth in diverse regions of Afghanistan while reinforcing cultural identity and promoting social cohesion.
Ensuring security, maintaining social stability, and safeguarding natural resources and cultural heritage are critical prerequisites for the sustainable development of tourism in Afghanistan. Furthermore, the implementation of supportive policies, targeted marketing strategies, and the promotion of cultural exchanges between tourists and local communities can enhance and elevate its appeal as a tourism destination. Nevertheless, the current circumstances, characterized by unstable security and the international community’s lack of recognition of the Taliban government, have rendered investors and tourists exceedingly cautious. Despite this, the travel of foreign tourists to Afghanistan demonstrates that a significant number of international visitors are keen to explore and experience this country. These journeys suggest that Afghanistan is poised for resurgence in its tourism industry.
In summary, by embracing a holistic and sustainable strategy, collaboration among governmental bodies, the private sector, and local communities, along with the intelligent utilization of available resources, Afghanistan has the potential to follow a balanced and sustainable development trajectory within the tourism sector.
Follow us on social media:
Telegram
X
Facebook