Review of Afghanistan developments
On April 17, 2025, the Supreme Court of Russia announced the removal of the Taliban from its list of terrorist organizations and lifted the ban on its activities. It is important to note that this decision was made after two decades of classification Taliban as a terrorist organization by Moscow.
There are various reasons for this, as the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs has stated that Moscow is currently seeking to strengthen mutually beneficial relations with Afghanistan in all areas, including combating terrorism and enhancing trade and investment cooperation with Kabul, particularly in light of Afghanistan’s strategic position in future energy and infrastructure projects.
These statements effectively decode Moscow’s recent decision, suggesting that geopolitical developments and geo-economics consequences in the region have heightened Afghanistan’s economic significance for Moscow.
In contrast, the Taliban government’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs issued a statement welcoming Russia’s decision to remove the group from the list of terrorist organizations, asserting that this represents a significant advancement in strengthening political and economic relations between the two countries.
Expansion of bilateral trade
Russia’s decision to remove the Taliban from its list of terrorist organizations is intertwined with the economic interests of both Moscow and Kabul. In this context, Russia was the first country to open its trade representative office in Kabul following the Taliban’s rise to power in August 2021. Furthermore, Moscow has expressed its interest in utilizing Afghanistan as a transit hub for transporting Russian gas to Southeast Asia.
Furthermore, Russia’s economic interests in Afghanistan are closely linked to its desire to exploit the strategically significant mineral resources found in the country, which cannot be invested in without a rapprochement with the Taliban. Russia has also expressed interest in ambitious infrastructure projects in Afghanistan, such as the Turkmenistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan-India gas pipeline, known as TAPI, and the rail corridor connecting Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, and Pakistan, referred to as the Trans-Afghan project.
- Amid the Western sanctions against Russia, Moscow is seeking to open its doors to more countries, with Afghanistan likely being one of the options. This is reflected in the significant increase in bilateral trade between the two nations in 2023, which has quintupled compared to 2022, surpassing one billion dollars. Furthermore, this figure is expected to rise even more in the near future.
The relative stability of Afghanistan under Taliban rule has sparked international competition for its emerging market and untapped resources. The World Bank had projected a 2.7% economic growth for the year 2024, and according to a recent report from this international organization, Afghanistan’s economy is expected to grow by 2.5% in the fiscal year 2024-2025, despite a decrease in international aid. Consequently, Russia has developed a plan to increase its trade with Afghanistan to $3 billion by 2025, with a target of reaching $10 billion by 2030.
Moscow has also facilitated the participation of representatives from the Taliban government at the St. Petersburg Economic Forum in 2022 and 2024, as well as at the International Economic Forum ‘Russia and the Islamic World’ in 2024. Additionally, a high-level delegation led by Mullah Abdul Ghani Baradar, the Deputy Prime Minister for Economic Affairs of the Taliban government, is scheduled to attend the ‘Kazan‘ economic meeting this month, during which the ‘Joint Economic Group of Afghanistan and Russia’ will convene. The aim of this collaboration is to finalize agreements regarding the transit of Russian gas through Afghanistan, with discussions reportedly focusing on the transfer of 50 million cubic meters of liquefied gas through the country.
Overall, Russia’s negotiations and interests indicate that there is potential for Russian investments in Afghanistan, particularly in the energy and mining sectors, as well as the opportunity to transform Afghanistan into one of Russia’s agricultural product markets.
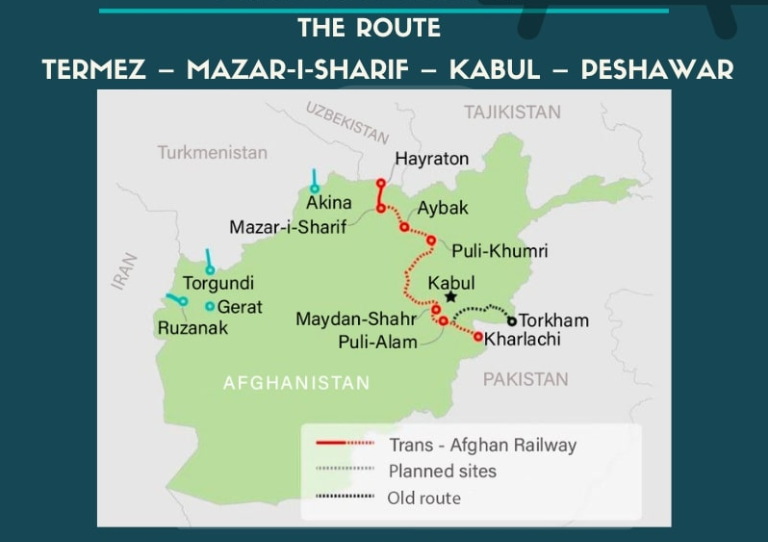
The significance of the Afghan transit railway corridor
Among the various economic and geopolitical factors influencing the relationship between Moscow and Kabul, the Trans-Afghan railway corridor may hold significant importance. In recent years, landlocked Central Asian countries have sought access to the ports of Pakistan or Iran to expand their global trade. One of the strategies these nations have pursued is the establishment of the Uzbekistan-Afghanistan-Pakistan railway corridor (Trans-Afghan), with an estimated budget of $4.8 billion.
Despite the strategic significance of this project, there has been little substantial progress in its development due to financial and security reasons. Recently, Russia utilized Iran’s railway network for transporting its cargo to Pakistan, which is part of the eastern section of the North-South Corridor.
Related Articles:
Results of removing the Taliban from Russia’s terrorist list
Russia’s perspective on Afghanistan and Taliban
It is important to note that last year, Kazakhstan and Turkmenistan joined the Trans-Afghan Corridor, and notably, Russia also announced its participation. Following Moscow’s entry into this initiative, numerous discussions have taken place between Russia and Central Asian countries regarding the Trans-Afghan project. Although the eastern section of the North-South Corridor could serve as a suitable link between Eurasia and South Asia, recent developments have demonstrated that reliance on a single route can have negative consequences. Therefore, Moscow is seeking to diversify transit routes in Asia, which has become increasingly significant due to Western sanctions.
Conclusion
The anticipated decision by Moscow to remove the Taliban from its list of terrorist organizations is expected to be a significant step towards strengthening bilateral relations between Moscow and the Taliban government in the near future. The Taliban aims to elevate its relationship with Russia to a new level of cooperation and to ease visa restrictions.
Economically, it is anticipated that Russian investments in Afghanistan will increase in the near future, and trade exchanges will also be strengthened, as evidenced by a 52% rise in Russia’s liquefied natural gas exports to Afghanistan in January and February 2025. In this context, it is expected that gas supply to Afghanistan will continue to grow in the coming years. Furthermore, Afghanistan’s geographical position offers a suitable foundation for bilateral cooperation, particularly within the framework of the Trans-Afghan Corridor.

















