Review of Afghanistan developments
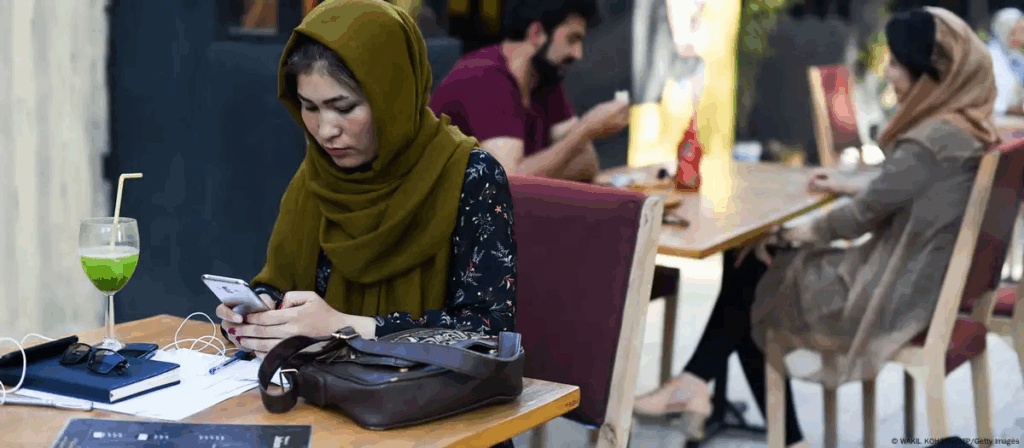
The media advancements of the 21st century, particularly the growth of social networks, have established a new platform for the portrayal and storytelling of Afghan migrants. These migrants, recognized as one of the largest groups in the region, have utilized this platform to share their lived experiences, advocate for social issues, and redefine their collective identity. This environment has enabled them to transition from being mere subjects of the narrative to active participants in it, and by producing textual, visual, and audio narratives, they are able to showcase new depictions of their lives; depictions that at times stand in contrast to traditional portrayals in the mainstream media.
Prior to the advent of the digital era, Afghan migrants were predominantly portrayed in host media through stereotypes, including that of inexpensive labor, war-affected individuals, or menacing refugees. Their stories were largely controlled by media organizations that frequently approached the issue of migration from either a compassionate or security-oriented viewpoint. Nevertheless, the rise of social media has disrupted this control. The second and third generations of Afghan migrants, particularly the youth and women, have now seized the opportunity to share their narratives directly via platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, TikTok, and Telegram. In this digital environment, they not only discuss the challenges associated with migrant life but also highlight the vibrant aspects of their existence, ranging from academic and artistic achievements to cultural and social engagements. This shift has resulted in a redefinition of the role of migrants within the host society and a restoration of their sense of human dignity.
Nonetheless, comprehending this phenomenon is not solely reliant on recognizing its beneficial aspects. While social networks can serve as instruments for empowerment, raising awareness, and facilitating self-expression, they also possess the potential to transform into a domain of distortion and exploitation for political purposes. Depending on the manner in which they are created and disseminated, digital narratives can function as both a medium for reconstructing identity and a space for perpetuating discrimination. The algorithms of these platforms and the underlying power dynamics of social networks often dictate which voices are amplified and which narratives are sidelined.
From this viewpoint, the significance of digital storytelling among Afghan migrants is not solely in the content created, but also in comprehending the power dynamics, various discourses, and methods of representation within the realm of new media. Social networks can transform into a venue for constructive self-expression and shared awareness only when both migrant activists and their audiences recognize and critically analyze the framework of this environment along with its cultural and social consequences.
The influence of visibility and the creation of alternative narratives through social media platforms
In this context, young individuals, particularly Afghan migrant women, have managed to construct an internal narrative through the creation of everyday content, ranging from brief videos to analytical podcasts; a narrative that, in contrast to stereotypical portrayals, is multi-faceted, varied, and rooted in their actual experiences. These unplanned narratives, articulated in straightforward yet meaningful language, have changed the experience of migration from a condition of silence into an engaging dialogue.
When Afghan migrants share their personal stories, they confront the prevailing narrative of discrimination and pity perpetuated by the host media. Through their accounts of education, career achievements, and even the mundane aspects of daily life, they demonstrate that they rise above the typical portrayal of migrants. This has slowly contributed to the development of a collective awareness among migrants; an awareness rooted in self-assurance and the recognition of the plurality and cultural diversity present within Afghan society in exile.
On the other hand, it is important to recognize that this visibility has evolved into a new arena for competition. In addition to original and critical narratives, there are instances where narratives are created that, in their quest for greater attention, inadvertently perpetuate the same outdated stereotypes. Consequently, social networks serve not merely as instruments for freedom of expression, but also as platforms for the ongoing redefinition of power, meaning, and identity. This dynamic illustrates that the digital narrative of Afghan migrants is not a fixed entity; rather, it is in a state of continuous interaction with the cultural, economic, and political frameworks of the host society.
Ultimately, social media and the digital realm present Afghan migrants with opportunities for both resistance and reconstruction, while also posing risks of misrepresentation and consumerist portrayals. Consequently, the significance of this space extends beyond mere visibility; it encompasses the migrants’ capacity to influence meaning and craft their own stories. If these narratives are developed thoughtfully and in relation to their authentic and collective experiences, they can contribute to a broader project of narrative justice.
The digital narrative and the reformation of collective identity during migration
For Afghan migrants, social media serves not only as a communication tool but has also evolved into a platform for shaping and redefining their collective identity. In circumstances where migrants encounter structural discrimination, ethnic labels, and legal limitations within host societies, the digital narrative empowers them to forge a new sense of “we”; a collective that is neither entirely severed from their homeland nor wholly absorbed into the host culture. This intermediate identity, central to the migration experience, is manifested in cyberspace through the sharing of memories, photographs, poems, dialects, and daily rituals, gradually transforming into the cultural and symbolic capital of migrants.
In numerous instances, Afghan migrants residing in Iran, Pakistan, Europe, and North America forge a collective memory through social networks. These recollections encompass childhood experiences in Afghanistan, narratives of escape, challenging periods of uncertainty, and joyful moments during migration; collectively, they form an emotional landscape of migrant existence. The sharing of these memories not only enhances the feeling of belonging but also fosters a unique form of extra-spatial empathy among migrants across various regions of the globe. In this regard, social networks have evolved into a conduit connecting the past, present, and future; a pathway that enables migrants to reconfigure their identities within a transnational and multicultural framework.

Afghan migrants, while engaging with the host culture and reflecting on their collective memory, reinterpret their values, beliefs, and symbols via social networks. This process of re-evaluation in the digital realm occurs daily: through discussions regarding the Persian and Dari languages, comparisons of marriage customs, or even the everyday humor that highlights cultural differences, which in turn reinforces the connection among migrants.
Moreover, collective representation within the digital realm significantly contributes to the restoration of self-confidence. Migrants who once felt marginalized or overlooked can now observe the achievements, initiatives, and uplifting stories of their counterparts. This collective experience of recognition fosters a heightened sense of self-assurance and unity, facilitating the establishment of support networks and centers of collective action. Indeed, online platforms have progressively evolved from mere individual expression to serve as instruments for cultural and social organization.
Nevertheless, the reconstruction of identity is not always consistent and coherent. In certain instances, ethnic, linguistic, or class distinctions among Afghan migrants are mirrored in social networks and can even result in the perpetuation of internal divisions. Nonetheless, this very process of dialogue and disagreement is integral to the dynamics of collective identity, illustrating that the Afghan migrant community is transitioning from a state of passivity to a heightened self-awareness. In conclusion, the digital narrative for Afghan migrants serves, among other purposes, as a vibrant process of collective self-construction that transcends geographical boundaries and has facilitated a redefinition of the migrant’s relationship with himself, with others, and with his past.
Opportunities and challenges for Afghan refugees on social media
– Creating solidarity networks
Social media has enabled Afghans to engage with one another, establish support networks, and even initiate civic campaigns. For instance, online campaigns advocating for the right to education for Afghan children or protesting the limitations imposed on Afghan society within Afghanistan have garnered significant attention throughout the region.
– Risk of political abuse
At the same time, Afghan narratives are occasionally appropriated by various governments and organizations. For instance, certain narratives are utilized to highlight the necessity for humanitarian assistance or to rationalize restrictive policies. This indicates that digital narratives are at times employed within the realms of power and politics.
– The necessity for neutrality and reflection of reality in the Afghan narrative
For Afghan refugees, neutrality does not imply overlooking either suffering or accomplishments; instead, it involves offering a comprehensive perspective: detailing poverty and discrimination while also highlighting their culture, art, and social resilience. Neutral narratives have the potential to shift public perception away from stereotypes, facilitating equitable dialogue between Afghans and host communities, and lending authenticity to the refugee experience. By observing these narratives, researchers and civil society advocates can assist in achieving a balance between visibility and non-appropriation.
Related Articles
Khalilzad’s roadmap for changing Pakistan’s power structure
Assessment of the American delegation trip to Afghanistan
Conclusion
An examination of the digital narrative surrounding Afghan migrants on social media reveals that these platforms have evolved beyond mere communication tools; they now serve as arenas for the construction and redefinition of collective identity. This environment enables Afghan migrants to escape from silence and marginalization, ensuring their voices resonate within society, while also allowing them to portray a fresh perspective of their lives and experiences.
In general, social media provides Afghan migrants with the opportunity to reshape their identity in relation to their past, the host culture, and their shared experiences, enabling them to create diverse and authentic narratives. Achieving success in this endeavor necessitates that migrants are conscious of how to articulate their experiences, while also being mindful of the cultural and social ramifications of their narratives, as well as the ongoing link between individual experiences and collective frameworks. Only under these conditions can the digital realm serve as a liberating instrument, not only aiding in the enhancement of morale and empowerment among Afghan migrants but also offering a significant model for other migrant communities and facilitating equitable and respectful dialogue among various groups.