Review of Afghanistan Developments
The Chief Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court (ICC) has recently urged the judges of the court to authorize the issuance of arrest warrants for Mullah Hebatullah Akhundzada, the leader of the Taliban, and Abdul Hakim Haqqani, the chief judge of the Taliban government. The ICC serves as the sole legal entity empowered to issue arrest warrants for individuals accused of crimes against humanity. In addition, the Rome Statute defines that those who systematically discriminate against individuals based on gender and are identified as human rights offenders are deemed to have committed crimes against humanity. In addition, the Rome Statute defines that those who systematically discriminate against individuals based on gender and are identified as human rights offenders are deemed to have committed crimes against humanity.
It is important to highlight that is the first occasion the ICC has recognized gender discrimination-related human rights violations as criminal offenses.
Basis for the court’s judgment
The ICC has put forth allegations regarding its request directed at the leaders of the Taliban. Primarily, the court highlights the sentences imposed by the Taliban leader on women and girls in Afghanistan. From the court’s viewpoint, these sentences have resulted in systematic and organized restrictions on women’s rights. Furthermore, the court identifies Abdul Hakim Haqqani as the principal architect and developer of the fundamental doctrine that underpins the Taliban government’s enforcement of restrictive laws and regulations affecting women and specific segments of society, thereby designating him as an accomplice. Additionally, according to the statements made by the court’s special prosecutor, Karim Khan, other members of the Taliban will also be considered in this context.
The requests made in recent years have primarily been grounded in the laws and regulations established by the Taliban leader. Furthermore, a wealth of reports from Afghanistan, along with documentation from various organizations and individuals, has contributed to the foundation of these requests. Nevertheless, it is essential to consider the political motivations of certain nations, as well as the influence of human rights organizations and adversaries of the Taliban government, which may have played a role in this context. While the laws enacted by the Taliban leader, in collaboration with specific members of the Taliban government, such as Abdul Hakim Haqqani, may appear justified at first glance, the underlying complexities cannot be overlooked.
The Court’s Constraints in Enforcing Rulings
While the ICC is esteemed as the principal legal authority for probing war crimes and human rights violations, the feasibility of arresting the leader and chief judge of the Taliban government is hindered by two main factors. To begin with, the ICC does not possess the means to enforce its decisions through coercive measures, as the implementation of its rulings is contingent upon the actions of sovereign states. Moreover, some member nations of the ICC may refrain from executing the decisions of this international institution for political motives.
A significant limitation arises from the absence of several countries, particularly major powers like the United States of America, from this organization. This absence presents a considerable obstacle to the enforcement of the organization’s decisions. It is important to highlight that the two prominent Taliban officials subject to arrest warrants have not traveled to any member states of the organization and are unlikely to do so. Furthermore, the Taliban leader remains largely out of public view within Afghanistan. Consequently, the practical possibility of apprehending these two individuals is virtually nonexistent.
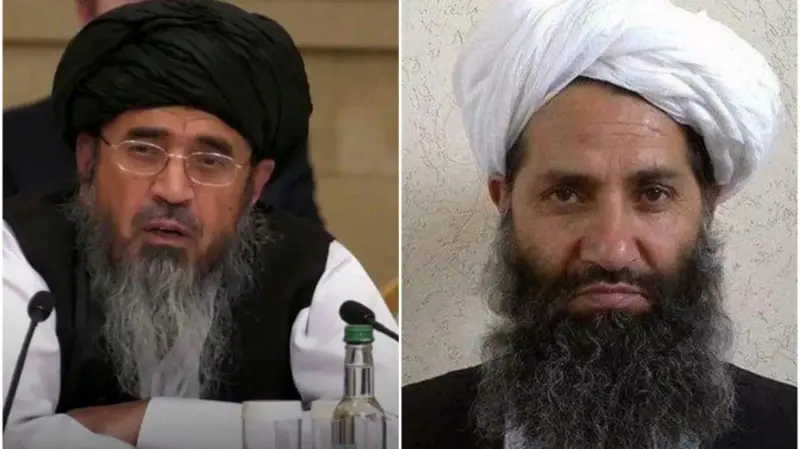

The Consequences of the ICC’s Ruling
The limitations surrounding the enforcement of rulings from the ICC , particularly in relation to the two Taliban leaders, present considerable obstacles. Should the court judges grant approval for such a request, the Taliban government would incur significant political and international costs. A likely initial consequence of this request is the potential for widespread despair and hopelessness among the Afghan people regarding their future prospects. The ICC’s actions could lead to a dismal perception within Afghan public opinion. The effects of this negative outlook are alarming, with one of the most significant repercussions being an uptick in migration, particularly among the elite class in Afghanistan.
A further implication of the ruling is the increasing discord among Taliban leaders regarding the approach to women’s employment and girls’ education. Certain high-ranking officials within the Taliban have voiced their discontent with the stringent regulations imposed on girls’ education, articulating their concerns in public addresses. Abbas Stanikzai, a notable figure within the Taliban who previously served as a senior negotiator in Doha and currently holds the position of deputy foreign minister for political affairs, has consistently condemned the harsh policies that inhibit girls from pursuing their education. While the Taliban leadership has thus far preserved a semblance of unity, developments such as the ruling from the ICC, coupled with Western sanctions, could signal the onset of a fracture within the Taliban’s cohesive framework.
A further alarming outcome is the potential to inflict additional harm on the Taliban government’s reputation within the global arena, which may result in some nations distancing themselves from Afghanistan. While it is expected that the majority of countries will dismiss such a request and will not take action, as seen in the case of the court’s ruling concerning Russian President Vladimir Putin and Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, there is a possibility that certain countries may decide to withdraw their support to Afghanistan in response to the same issue and ruling.